
Foreword
Purpose of this tutorial
The purpose of this tutorial is to provide the reader with a general view about 5GTANGO platform in the easiest and quickest way possible. Here you will find a brief explanation about what 5GTANGO is, how to install it, how to use it and how to get technical support if required. This tutorial is not an exhaustive guide document to all features of 5GTANGO, but rather an “umbrella” document that will guide you to the more extensive documentation if required.
1. Document structure
This quick guide is organized in the following manner:
- Section 1 (this section) is an introduction to the guide.
- Section 2 provides a general overview of 5GTANGO: what 5GTANGO is and for whom, its general architecture, and a brief description of its main modules, the Service Platform (SP) and the Service Development Kit (SDK) and the Validation and Verification (V&V).
- 3. Release Notes provides current 5GTANGO software release notes.
- 4. Quick guide provides a quickguide for installation and usage of SONATA components (SDK, V&V and Service Platform).
2. What is 5GTANGO?
5GTANGO is an agile service development and orchestration framework for 5G virtualized networks. It provides a programming model and a development tool chain for virtualized services, fully integrated with a DevOps-enabled service platform and orchestration system. 5GTANGO aims to support the programmability of software networks as well as the optimization of their deployments. Its modular design makes the SONATA service platform effortlessly customizable to meet the needs of different service providers.
5GTANGO provides a platform for supporting the lifecycle of virtualized networking services. In particular, network function chaining and orchestration are the target domains of SONATA.
Who is it for?
The 5GTANGO platform supports two main stakeholders in telecommunications service creation: service developers and service operators. 5GTANGO’s Network Service Development Kit (SDK) facilitates network service development for service developers. Such services are then deployed and run on 5GTANGO’s Service Platform. Through its extensive customization capabilities, the service platform allows communication service providers to adapt service provisioning to their specific environment and needs. 5GTANGO enables a DevOps workflow between the SDK tools and the service platform, which allows developers and operators to closely collaborate in providing an outstanding experience to customers. Also you have available the VnV for testing purposes.
2. General Architecture
The main architectural components of the 5GTANGO platform are shown in the figure below. In line with the support of service developers and service operators, SONATA distinguishes the two main components SDK and service platform. Services developed and deployed by this system run on top of the underlying infrastructure accessible to the SONATA system via Virtual Infrastructure Managers (VIMs), abstracting from the actual hardware and software.
Each of the three main components can be divided into a number of subcomponents, realized in a micro-service-based approach. Detailed information on the architecture and its components can be found in [https://5gtango.eu/project-outcomes/deliverables/2-uncategorised/31-d2-2-architecture-design.html].
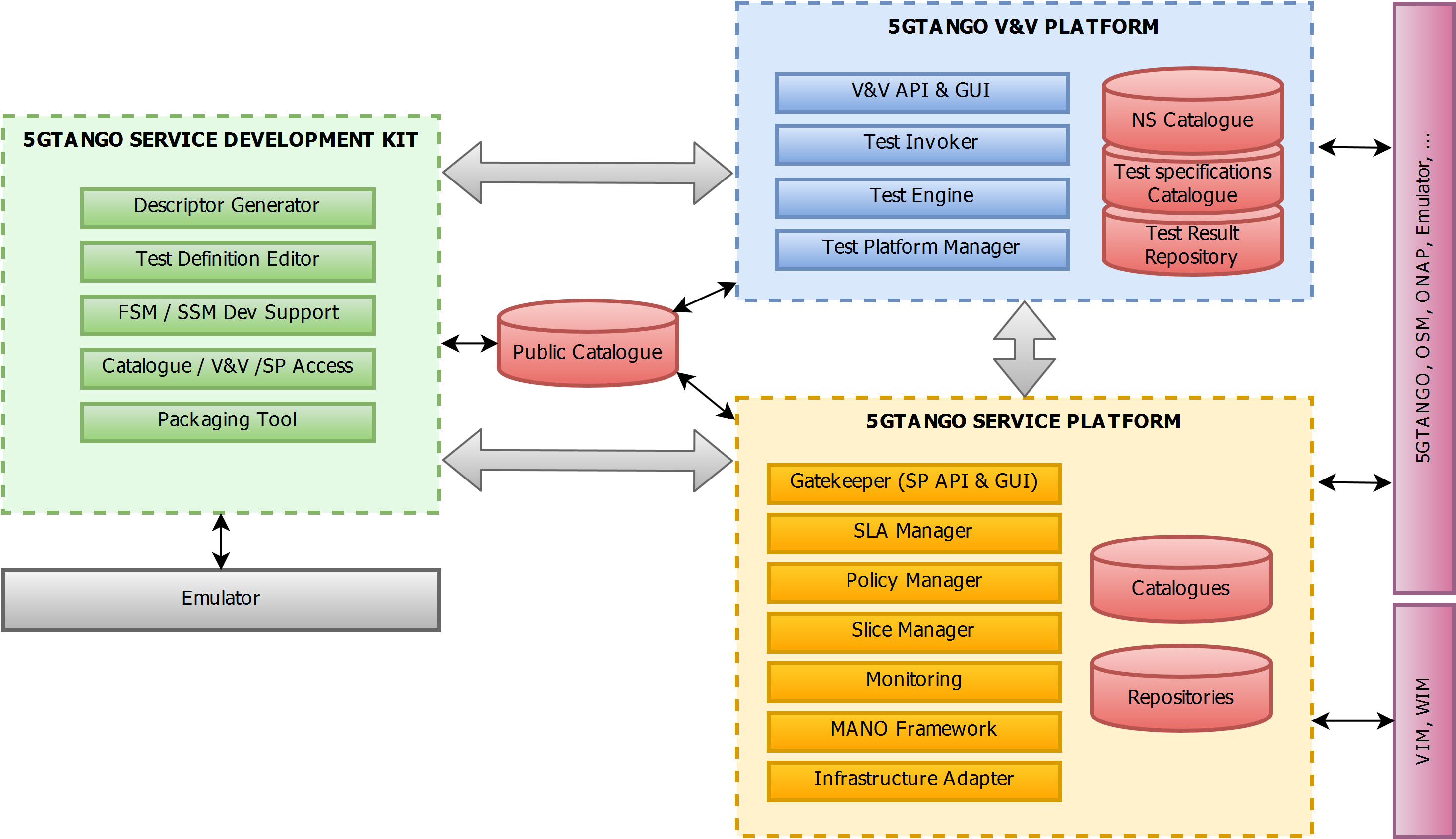
5GTANGO Modules
The 5GTANGOplatform consists of a number of software modules which together provide the required functionality for network service creation, deployment, and management. Most modules can be attributed directly to either the service platform or to the service development (SDK), according to their use. Some modules are cross-cutting and are used in both major components.
Service Platform
5GTANGO’s Service Platform (SP) is where:
- users are created, authenticated and authorized;
- packages, containing (network) services and (virtual network) functions descriptions, are on-boarded, validated and stored in the catalogue. A service or a function can bring with it a specific manager, which may change the default behaviour the SP has for specific aspect of that service’s or function’s lifecycle (e.g., placement, scaling, etc.);
- services from the catalogue are instantiated (with licences verified) and orchestrated, through the MANO, in the abstracted infrastructure;
- instantiation records are generated and stored, providing instantiation data to the other components;
- monitoring data is collected and securely provided on demand to the service developer, thus allowing quick and frequent service improvements;
- KPIs are collected, to show the overall business performance of the system.
The main modules of the SP are the following:
- Gatekeeper: controls and enforces whoever (and whatever) wants to interact with the SP and guarantees the quality of the submitted packages, by validating them against a schema (syntactically), the topology of the described service and it’s integrity;
- Catalogues: stores and manages (smart delete: only packages with services that do not have running instances can be deleted) package files, it’s meta-data as well as service’s and functions’ meta-data. The catalogues use the SONATA schema for their metadata as defined in SONATA schema;
- MANO Framework: the orchestrator, who manages each service’s lifecycle, including when the service and/or its functions bring specific managers with them to be used in certain segments of their lifecycle. Please note the clear separation between the two levels, the Network Function Virtualization Orchestrator (NFVO) and the Virtual Network Function Manager(VNFM) and Controller. This separation was originally recommended by ETSI, and it effectively corresponds to two very different levels of abstraction that is important to be kept separate;
- Infrastructure Abstraction: hides the complexity and diversity of having to deal with multiple VIMs and WIMs;
- Repositories: stores and manages service and function records, resulting from the instantiation, update and termination processes;
- Monitoring: collects (via monitoring probes), stores and provides monitoring data for the services and functions instances.
These are the highest level modules. Further details on each one of them can be found in each one of those modules GitHub’s repositories.
SDK
The service development kit (SDK) consists of the following main modules:
- Schemas: Schemas defining the structure and syntax of all descriptors within the project (e.g., for VNFs, network services, packages, SLAs, policies, …)
- Descriptor generation and project management: Tool for generating VNFD and NSD descriptors based on high-level information and for managing created NFV projects.
- Validator: Tool for validating generated descriptors and projects based on syntax, integrity, topology, or custom rules.
- Packager: Tool to create and unpack 5GTANGO packages
- Emulator: emulation platform to support network service developers in locally prototyping and testing complete network service chains in realistic end-to-end multi-PoP scenarios
- Benchmarker: Tool for fully automated VNF and network service benchmarking and profiling.
VnV
The Validation and Verification (VnV) platform consist of the following modules:
- Gatekeeper: This is the 5GTANGO Gatekeeper Verification and Validation platform specific components repository, which closely follows its SP Platform counterpart.
- Planner: component to coordinate the verification and validation activities of 5G Network Services. The Planner acts as the main manager for the V&V test requests. It is responsible for test plans management, sequencing, and triggering requests of the corresponding test requests.
- Curator: The Curator acts as the intermediate module between the Planner and the Executor for all V&V tests activities. It is responsible for processing a Test Plan, preparing the SP environment for tests, processing instantiation parameters, triggering the execution and cleaning up the environment afterwards.
- Executor: This is a 5GTANGO component to execute the test suites for 5G Network Services.
- Platform Adapter: An Adapter for VnV to talk to various Service Platforms. Out of the box support is currently for the following service platforms: SONATA, OSM, ONAP.